Before leaving this page, you should:
Click through this Powerpoint presentation in order to learn how to develop keywords to search a database.
As you start searching for your topic, you might realize that your topic is too broad or too narrow. It is important to be flexible on your topic.
Broad Topics
Broad topic example: My paper is on psychological disorders.
This topic is too broad, which means you will find too much in the database on your topic. It will be hard to focus your paper. You will have to narrow it down.
Narrowing Chart
| General topic: | Domestic Terrorism |
| Time span: | Last 3 Years, Last 5 Years, |
| Place: | United States, Major American Cities, Rural America etc. |
| Person/Group: | Youth, College Age, Elderly, Certain Race or Ethnicity, etc. |
| Aspects: | Effects on Public Policy, Intelligence, Federal and State Agencies |
Narrowed topic: How has domestic terrorism impacted federal and state policy over the last 5 years?
Narrow Topics
Narrow topic example: What is the effect of Red Cross blood drives on adults with hemophilia in the town of Farmville, NC?
This topic is too narrow, which means you will not find enough in the database on your topic. There may not be studies that look at Farmville, or there may not be many hemophiliacs in the town. Unless you plan to do a study yourself, you will have to broaden it.
Broadening Chart
| Specific topic: | What is the effect of Red Cross blood drives on adults with hemophilia in the town of Farmville, NC? |
| Alternate Focus: | Remove Red Cross, blood donation process, sociological impacts |
| Alternate Place: | rural North Carolina, southeast United States, etc. |
| Person/Group: | car accident victims, cancer patients, etc. |
| Aspects: | Donors, blood types, use of blood in hospitals, etc. |
Broadened topic: What is the effect of blood drives in the southeast United States?
Boolean Operators AND, OR, and NOT connect each keyword and/or keyword phrase in a statement such as: What is the relationship between United States intelligence operations and counterterrorism?
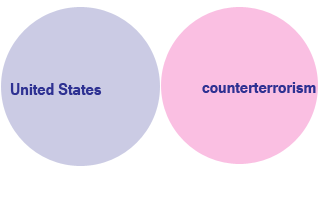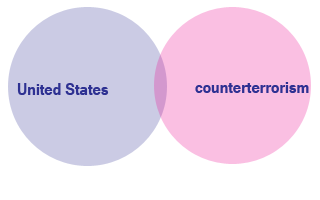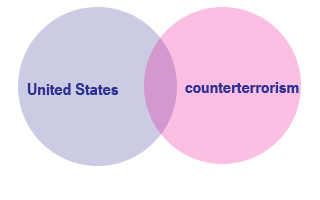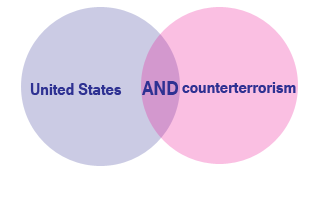
In the following examples, circles and areas in the Venn Diagrams that appear purple are returned as search results by the database.
Use AND to narrow a search strategy and to look for two or more terms in your result.
Example: United States AND counterterrorism
Use OR to broaden a search and to find either or both concepts in the result.
Example: counterterrorism OR counter terrorism
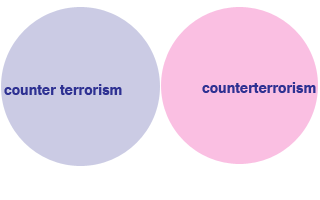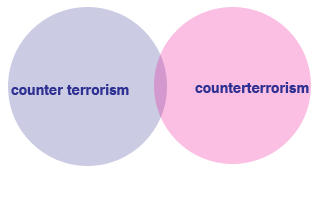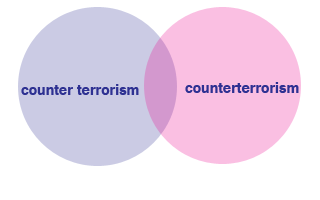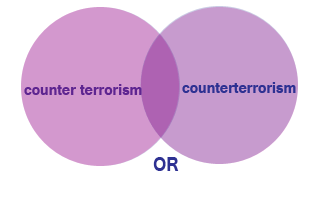
In this case, every article with either "counter terrorism" or "counterterrorism" is returned in the list of results.
Use NOT before a term to exclude it from your result.
Example: intelligence NOT IQ
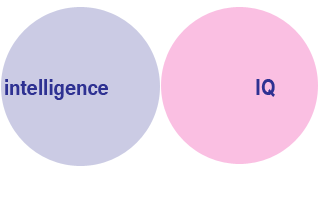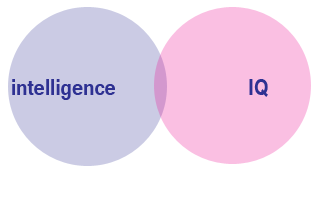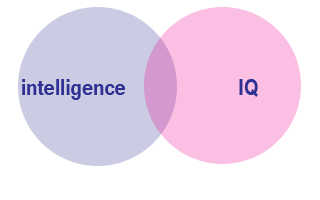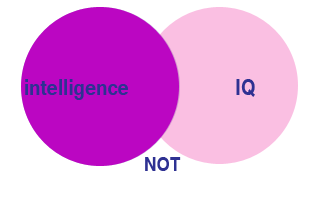
In this case, only articles with the subject of intelligence are returned in the search, but those dealing with IQ are not returned.
Use nesting to build a more complex search by putting keywords and/or phrases in parentheses to determine their relationship when more than one operator is used.
Example:
(United States AND intelligence) AND (counterterrorism OR counter terrorism)